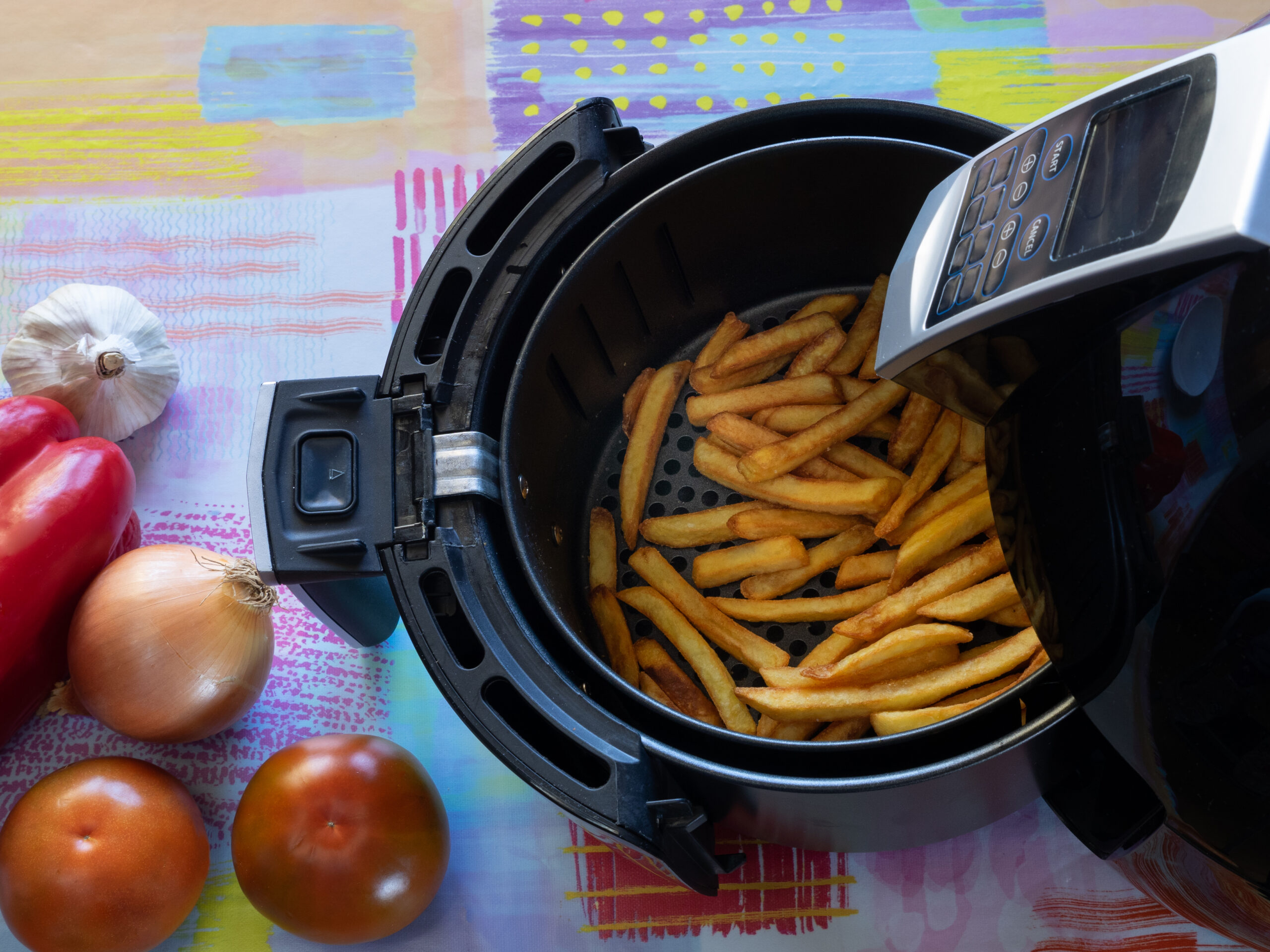

An air fryer is a kitchen appliance that uses hot air circulation combined with a minimal amount of oil to cook food. The air fryer’s heating mechanism involves a powerful fan that circulates hot air around the food, providing even, quick, and thorough cooking. The air fryer’s heating element, located at the top, produces heat, which is then distributed by a fan throughout the cooking chamber.
Air fryers are versatile appliances that can be used for various cooking techniques, including air frying (obviously), baking, toasting, and more. Their quick cooking capabilities and efficient heating mechanisms save users some much-needed time and energy. They’re often compact and portable, making them suitable for small kitchens, dorm rooms, or even camping trips. The easy-to-use controls and dishwasher-safe accessories make cleaning and maintenance a breeze. So, how do these appliances actually work?
Unlike traditional frying methods that rely on oil for heat transfer, air fryers use a powerful fan to circulate hot air around the food. The convection process in an air fryer begins when you preheat the appliance to your desired temperature. Once the air inside reaches that set temperature, the fan kicks in and starts circulating the hot air throughout the cooking chamber. As the hot air moves around the food, it transfers heat energy to the food’s surface, creating a browned exterior.
However, there are a few drawbacks. The high-speed air circulation can sometimes lead to food items drying out, especially if they’re not coated properly. The rapid movement of air can also cause lightweight ingredients to be blown around, potentially affecting the cooking consistency.
In an air fryer, there’s a heating element located above the food basket. This heating element emits infrared radiation, which heats up the air surrounding the food. The concentrated heat from the infrared radiation ensures that the food is thoroughly and rapidly cooked.
As the heated air circulates around the food, it transfers heat directly to the surface, creating a Maillard reaction. This reaction is responsible for browning and crisping the food, giving it that desirable texture and taste. The radiant heating mechanism ensures that the food is cooked from all angles, generally eliminating the need for flipping or turning the food during the cooking process. This method is renowned for its ability to quickly sear and brown food, giving it a delicious caramelized exterior, similar to how a grill operates.
Conductive heating involves the transfer of heat through direct contact between the food and a hot surface. In the case of air fryers, this hot surface is typically the cooking basket or tray. When the food is placed in the basket or tray, the heat is rapidly transferred to its surface, resulting in a Maillard reaction, as explained earlier.
One common method is the use of electric heating elements placed near the cooking surface. These elements rapidly heat up, creating a hot surface for the food to come into contact with. This method is especially efficient for cooking items that require a crispy bottom, like french fries or chicken wings, though it may not distribute heat as evenly as convection heating, which could result in uneven cooking.
Understanding the heating mechanisms in air fryers allows us to appreciate their efficiency and versatility in the kitchen. By utilizing a combination of intense heat, convection, and rapid air technology, air fryers can deliver delicious and healthier meals in a fraction of the time compared to traditional cooking methods.
In conclusion, while air fryers primarily utilize convection heating, understanding the differences between convection, radiant, and conductive heating mechanisms can help you make informed decisions about your cooking preferences. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, so it’s important to consider the type of food you are cooking and your desired outcome when using an air fryer.
Don't just make desserts, make THE desserts of all time with fancy gadgets you're going…
Looking to spruce up your kitchen without breaking the bank? Don't worry! We've got some…
Move over, meat-and-cheese boards—there is a new charcuterie showstopper in town! It's these charcuterie tacos!…
Baking isn’t just about following a recipe, it’s about creating something warm, comforting, and joy-filled.…
Are you planning the ultimate group dinner for your girls? Whether you're hosting a cozy…
Looking for ways to make your day-to-day tasks less of a headache? We've rounded up…
This website uses cookies.